How to Run Nodes and Their Role in the Core Blockchain

In the dynamic realm of distributed ledger technology, nodes are the silent architects shaping the decentralized landscape of a blockchain. Understanding the intricacies of these nodes is not merely a technical nuance but a key to clarifying the very essence of blockchain's sustainability, resilience and transparency.
Join us as we embark on a journey to demystify the role of blockchain nodes, explore their functions and significance in the intricate tapestry of distributed ledgers, and learn how to run your node on Core Blockchain.
Node as a Decentralized Database Server
In contrast to conventional centralized databases and consensus mechanisms that rely on staking or permissioned blockchains, where one entity or a weighted average of nodes exercises control over the entire dataset, a genuinely decentralized proof-of-work blockchain functions as a network of nodes where each node actively engages in the storage and validation of data, ensuring equal participation and distribution of validating data.
In a blockchain network, every node acts as a small database server. These nodes are usually spread across the globe, contributing to the network's decentralized nature. Each node holds a copy of the entire blockchain, ensuring data redundancy and reliability.
Distributed Immutable Ledger
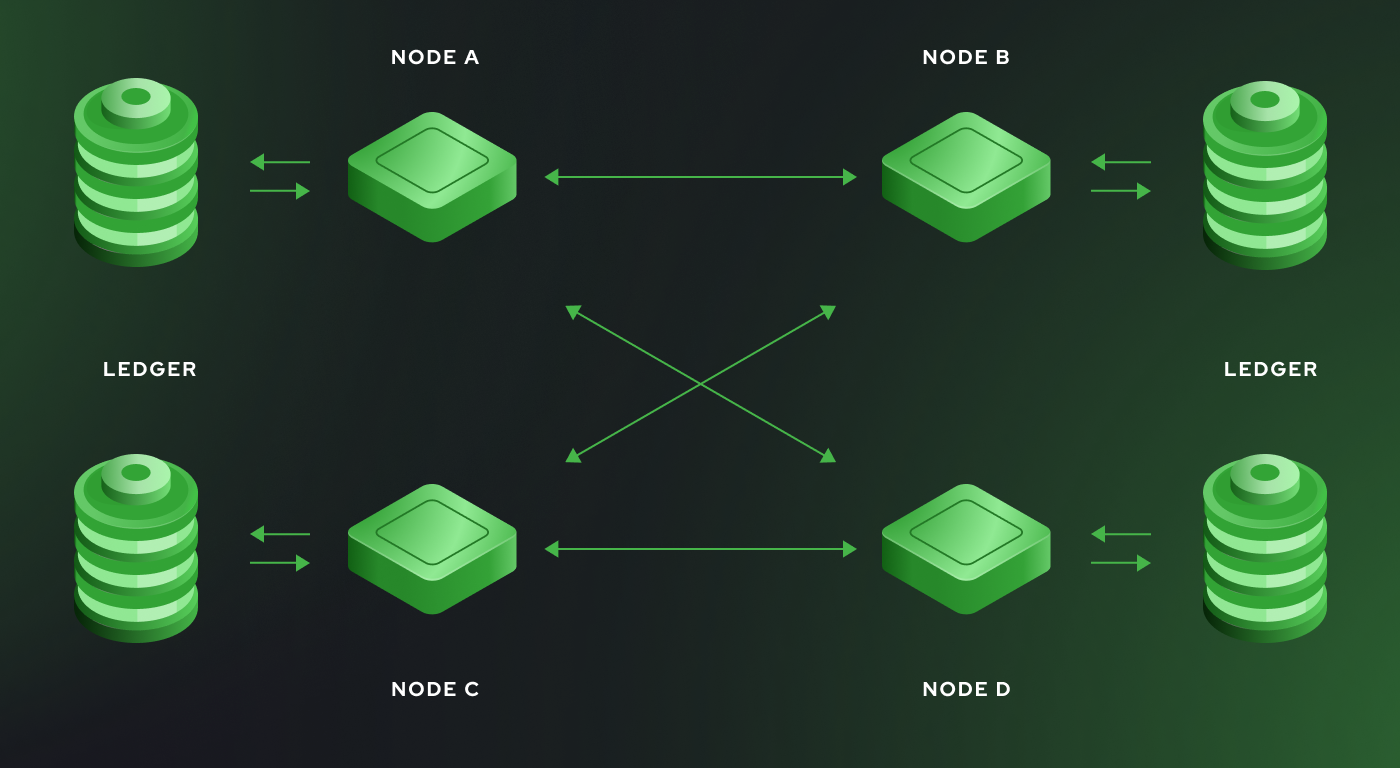
Conception of a Node
In general a node is a computing device (like a desktop computer, raspberry pi, laptop, or server) that runs special client software and is connected to the blockchain network. Each node has the capability to perform various functions, depending on its type and the architecture of the blockchain.
CoreBlockchain currently uses the Go-core client. It’s open source and is available on GitHub.
Consensus Mechanism
A consensus mechanism is a routine used in blockchain systems to achieve distributed agreements about the ledger's state. These mechanisms ensure that all nodes agree on the state of the ledger, making the network resistant to fraudulent activities. There are different kinds of consensus mechanism algorithms, each of which works on different principles.
CoreBlockchain utilizes a Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism which requires an active participant in the network,referred to as a miner, to solve a complex computational problem in order to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain, and obtain proper rewards.
Nodes and their primary functions
- Establish and maintain peer-to-peer connections with other nodes.
- Validate incoming and/or new blocks and new transactions.
- Propagate information about new transactions and new blocks to other peers.
- Provide application interfaces (like RPC) to software (like crypto wallets, utilities, custom scripts,etc.) for accessing main blockchain functions (like getting balances, sending transactions, smart-contract interactions, mining activities, etc.).
- Store various types of blockchain data, including blocks, transactions, fingerprinted data and state data in an efficient manner using special data structures (like prefix trees). The database should efficiently handle the ever-growing size of the blockchain.
Nodes and their optional functions
Optionally, if it is configured, a node can aggregate transactions into a new block and seal this block performing the mining process (solving a complex computational problem of finding the proper nonce for the block hash). In Core Blockchain each node can act as a solo-miner (currently with a very low probability of rewarded success)
For a better mining experience, we recommend connecting your computational facilities to one of the existing mining pools.
Mining pools and their functions
A mining pool is a special 3rd party software similar to a supercomputer that is installed on a set of servers, a mining pool is connected to the special upstream node which creates a block that should be mined, receives the resulting nonce from the pool, and seals this block.
On the flip side, the pool welcomes connections from miners using the stratum protocol and distributes the computational workload among them. Pools handle accounting for the hashrate and individual miner efforts, ensuring proper rewards are assigned and paid out regularly, in the case of Catch That Rabbit every 4 hours.
Nodes, pools, and client interactions
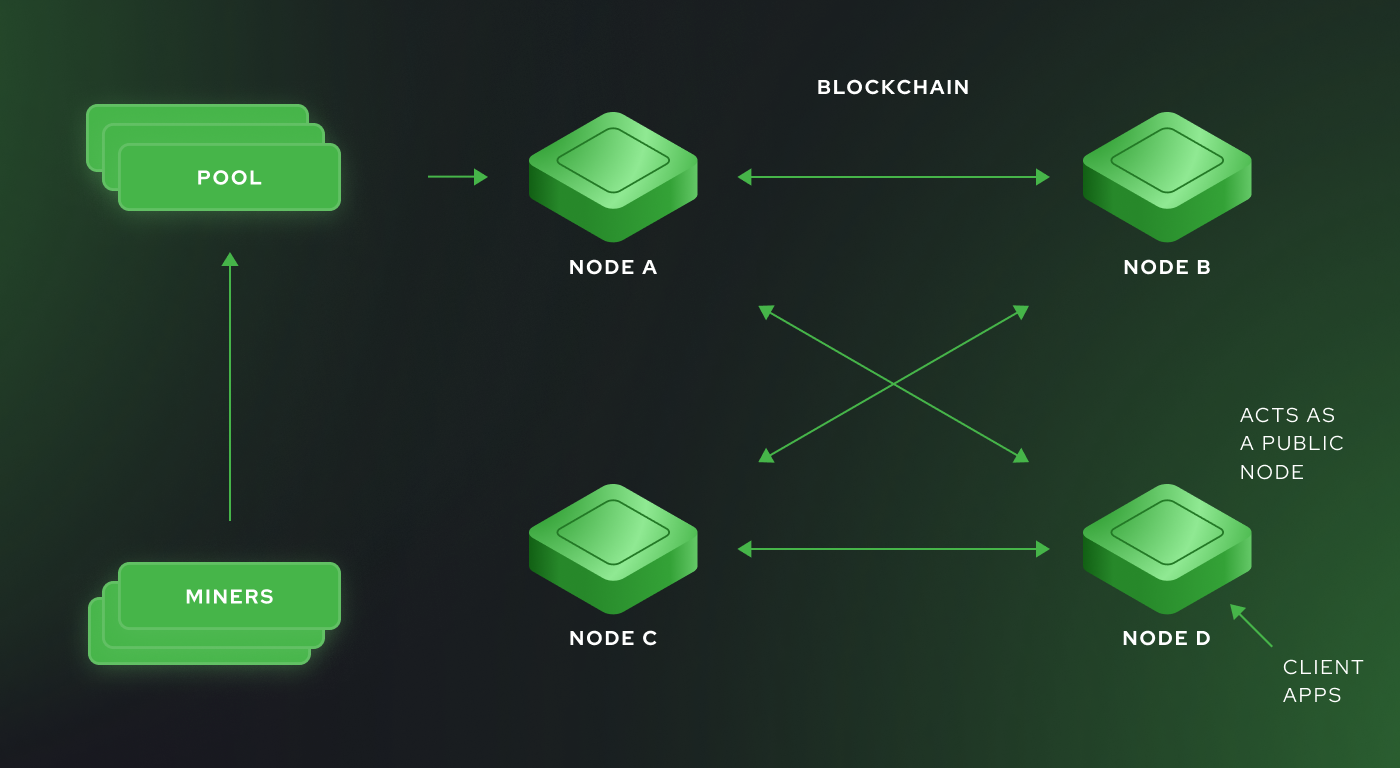
How to run your own node and participate in CORE consensus
Hardware requirements
- Dedicated machine or VPS with at least 2 CPU cores available.
- At least 8GB of memory.
- At least 16GB of free space on SSD (Current DB size is 4.7 GB).
- Fast network connection to the Internet.
- It is not recommended to place many Go-core nodes in the same local network behind the NAT.
Installation
- Download the latest release from GitHub - Gocore.
- Ubuntu Linux is recommended but you have the option to run it on Windows (just download the appropriate binary).
- Place executable Go-core binary to your home directory and check/setup proper file attributes/linkage.
- To run in interactive console mode type
sudo ./gocore --syncmode "full" --datadir=./mydatadir console(here mydatadir is your favorite location for Go-core database and wallets). - In order to separate warnings and other messages you can redirect logs output:
sudo ./gocore --syncmode "full" --datadir=./mydatadir console 2> /home/myhome/gocore.log
Tips, Linux Command
- You can use screen Linux command to run Go-core client in the background.
- You can setup system service to run Go-core as a daemon on Ubuntu.
- Go-core client has command line options compatible with the command line options of Geth Ethereum client.
- Console commands and features are compatible with Geth software with one exception:
ethnamespace was changed toxcb. For example, to check the balance you could use thexcb.getBalancecommand instead ofeth.getBalancein Geth. Reference for using the interactive console.
Collectively as a Community
We all play a pivotal role in shaping the advancement of Core Blockchain, one node at a time.
The strength and decentralization of Core Blockchain hinges on its nodes. By installing nodes, you are making a substantial contribution to the growth of blockchain and endorsing decentralization. Your support plays a vital role in unlocking the transformative potential of Core Blockchain, serving as the backbone of this groundbreaking technology.
We encourage everyone who believes in the Core Blockchain and the future of genuinely decentralized proof of work networks to install and maintain a Core Blockchain Node.
Thank you to everyone in the Core Community for your participation building a sustainable and resilient decentralized future.